Sunday, 19 February 2012
Friday, 17 February 2012
Motherboard Definition and Terminology
What is a Motherboard?
This page contains motherboard definitions and terminology to help your understanding of what motherboards are and the role they play in your computer system.
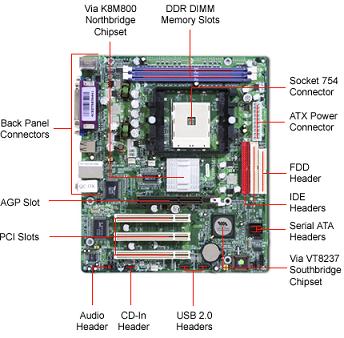
A motherboard is the main printed circuit board in a computer that carries the system buses. It holds the sockets to which all other components are connected, such as the processor, memory modules, graphics card, sound card, and all other components and peripheral devices.
The motherboard's role in a computer system can easily be described by comparing it to the human body's nervous system. The wires (nerves) on the motherboard transfer data to all the other components.
Three well known motherboard manufacturers are Asus, Abit, Intel, and MSI. Buying your motherboard from one of these brand names is always a good idea, as you will know you're getting a quality product.
After reading this motherboard definition, you shouldn't need to ask the question "what is a motherboard" ever again! For information on how to choose the best motherboard for your computer, see the article How to Choose the Best Motherboard.
Define RAM
Random access memory (RAM) is a form of computer data storage. Today, it takes the form of integrated circuits that allow stored data to be accessed in any order with a worst case performance of constant time. Strictly speaking, modern types of DRAM are therefore not random access, as data is read in bursts, although the name DRAM / RAM has stuck. However, many types of SRAM, ROM, OTP, and NOR flash are still random access even in a strict sense. RAM is often associated with volatile types of memory (such as DRAM memory modules), where its stored information is lost if the power is removed. Many other types of non-volatile memory are RAM as well, including most types of ROM and a type of flash memory called NOR-Flash. The first RAM modules to come into the market were created in 1951 and were sold until the late 1960s and early 1970s.
Other memory devices (magnetic tapes, floppy discs, CD's and DVD's) can access the storage data only in a predetermined order, because of mechanical design limitations.
What is a hard drive used for in computers?
What is a hard drive used for in computers?
Storage, storage and more storage! This is the only purpose of your hard drive.Your operating system and all of your software, music, movies, games and files are stored on your hard drive. Your hard drive can contain a phenomenal amount of information, to put the storage capacity into perspective a modern hard drive can contain the entire contents of your local library and have room left over for more!
But what is even more amazing is that we can run out of space!
In this digital age we rely heavily on our hard drives, games to home movies and every conceivable piece of software are stored within the device.
The amount of information contained on your hard drive is limited by its storage capacity. This is measured in gigabytes or terabytes.
The hard drive contained inside your computer can be replaced with a larger one if you are running low on space. Doing this will result in all your information and software having to be reloaded onto your new hard drive, that is assuming you have all the original disks for every piece of software and have all your personal files stored somewhere off your computer.
In reality this is not the best way to increase your storage space because most of us don't have all the original software disks and do not back up all our personal files.
A better way to increase your storage capacity is to purchase a second hard drive, this can be a second internal hard drive contained within your home computer or a stand alone storage device known as an external hard drive.
External hard drives
External hard drives are a convenient option for increasing the storage capacity on your computer system. They are easy to use as they simply plug into a USB port, and most operating systems will recognize the new hard drive and install the driver software automatically. All you need to do then is drag and drop the files you want stored onto your new external hard drive.External hard drives are a great way to keep your files safe from a computer failure. They are also useful for storing your music, movies, pictures, games and files as this will save valuable space on your internal hard drive leaving it free for the essential smooth running of your computer.
What is a hard drive and how does it work?
How does a hard drive work?Have a look at the diagram below, does that look like something you have seen before? A record player perhaps!

The platter is the magnetically coated disk that contains all the information encoded on your computer. This is spun by its own motor at speeds between 5,400 - 10,000 revolutions a minute.
The head moves along the platter on a cushion of air which is created by the fast spinning platter never touching the sensitive magnetic coated mirror finish. The actuator arm propels the head across the surface of the platter reading and writing information from different sectors up to 50 times a second.
Information can be stored, deleted and written over, making your hard drive phenomenally versatile.

The history of hard drives
 Its 1956 and you have decided to buy a brand new hard drive from IBM!Do you have the manpower to move it?
Its 1956 and you have decided to buy a brand new hard drive from IBM!Do you have the manpower to move it?Have you got a spare $150,000?
Prepared to pay a little air freight?
Welcome to your brand new IBM 305 RAMAC Hard disk drive with a stunning 5 megabytes storage capacity.The IBM 305 RAMAC is our smallest hard drive measuring only 16 square feet and weighing in just under a ton.Shipping available worldwide via airfreight, at buyers expense!
Thats enough mocking of old technology from me! This was the first commercial hard drive available and sold approximately one thousand units before the next model was released in 1962.
The 5 megabytes was considered an enormous amount of storage at the time. Today the average hard drive in a new home computer would contain a 500 gigabyte hard drive and cost around $100, that is one hundred thousand times more storage than the IBM 305 RAMAC hard disk drive of 1956 and over a thousand times cheaper!
By the 1980s smaller hard drives were being created with a storage capacity in the low gigabytes but with a hefty price tag of up to $800,000. I think most people were able to stay away from an impulse buy!
The 80s and 90s saw the beginning of the home computing era and an increased need for affordable storage. Hard drive technology advanced a huge rate through these years. At first in the early 1980s, home computers were being released with 10mb hard drives but by the late 1990s a home computer could have as much internal hard drive storage as 500mb.
One thing we can be sure of is that computer users will always demand more storage, and hard drives storage capacity will keep getting bigger and bigger to meet our ever increasing digital storage demands.
What is a hard drive? A permanent internal storage device for your computer
Defination of Computer
A. DEFINITION OF COMPUTER
The term computer has a broad meaning and is different for everyone. The term computer (computer) is taken from the Latin meaning computare count (to compute or to reckon).
According Blissmer (1985), the computer is an electronic device capable of performing several tasks, namely to receive input, process the input according to the instructions given, keep the commandments and the results of its processing, and provides output in the form of information.
Meanwhile, according to Sanders (1985), the computer is an electronic system to manipulate data quickly and accurately as well as designed and organized in order to automatically receive and store input data, process it, and produce output based on instructions that have been stored in the memory. And many more experts who are trying to define it differently on the computer. However, in essence it can be concluded that the computer is an electronic device that can receive input, process input, provide information, using a program stored in computer memory, can store programs and data processing, and works automatically.
B. COMPUTER SYSTEM
The main objective of the computer system is processing data to produce information that needs to be supported by elements consisting of hardware (hardware), software (software), and brainware. Hardware is computer equipment itself, is a software program that contains the commands to perform certain processes, and brainware are human beings involved in the operation and manage computer systems.
The three elements of the computer system should be interconnected and form a unity. Hardware without the software will not mean anything, just a dead object. Both hardware and software may stop working if there is no man who operate them.
C. COMPUTER STRUCTURES
Computer structure is defined as the ways of each of the components are interrelated. The structure of a computer is simple, can be described in the block diagram in Figure below.

where the CPU / processor, memory and I / O ports are located (installed) on the motherboard.
In summary, the computer system consists of three important components:
1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) / processor
2. Memory (RAM and ROM)
3. Input / Output
== Device (Input Tool) computer hardware that serves as a tool to enter data or commands into the computer.
== (Tool Output) computer hardware whose function is to display the output as a result of data processing. Output can be either hard-copy (the paper), soft-copy (to monitor), or in the form of sound.== I / O Ports This section is used to receive or send data out sistem.Peralatan input and output of the above connect through this port.== (Central Processing Unit) CPU is the brain of computer systems, and operational functions have two parts, namely:
- (Arithmetical Logical Unit) as the central data processor, and
- (Control Unit) as a controller of the computer work.
- Late Register
- Cache memory
- Main memory
- Secondary memory
== Data Bus routes transfer of data between modules in computer systems. Because at a certain time each channel can only carry 1 bit of data, then the number of channels determines the number of bits that can be transferred at one time. Data bus width determines the overall system performance. Its bidirectional, meaning that the CPU can read and receive this data via the data bus. Data Bus typically consists of 8, 16, 32, or 64 parallel lines.== Address Bus Used to indicate the location of the source or destination of data transfer process. At this point, the CPU will send the memory address to be written or dibaca.Address
bus usuallyconsists of 16, 20, 24, or 32 parallel lines.
== Bus is used to control the use and access to the Data Bus and Address Bus. Consisting of 4 samapai 10 parallel channels
From :- Varinder SaHeb
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)




